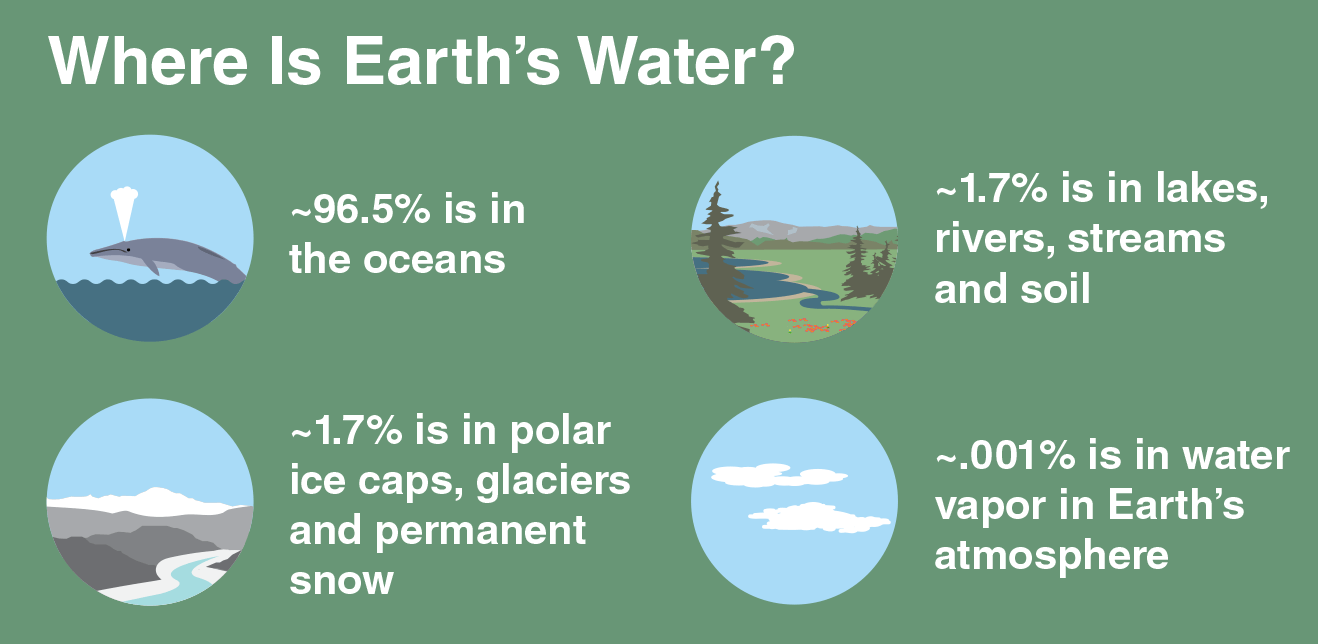
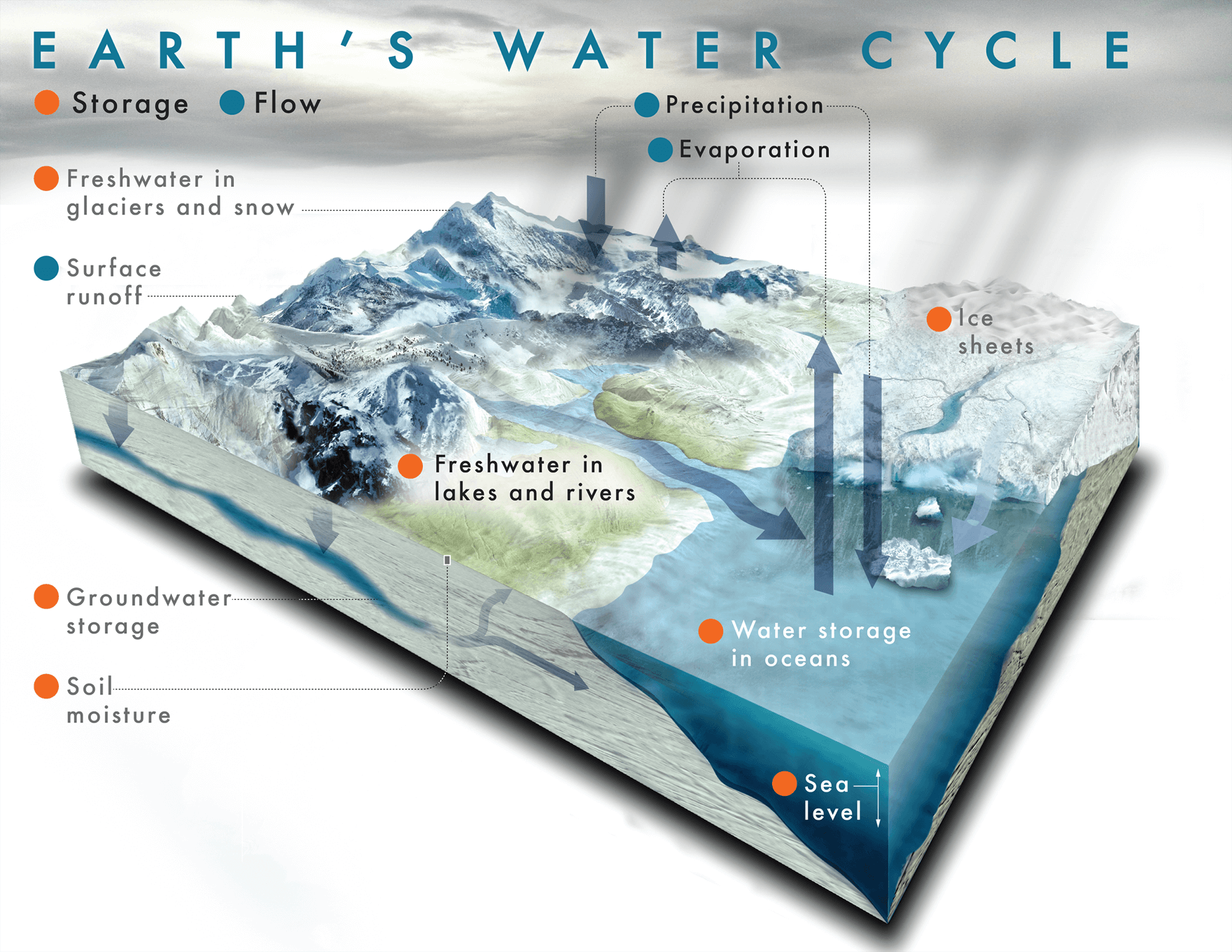
Aim; To look at the different ways we can prevent climate change in the future.
Name 3 fossil fuels?diesel coal natural gasWhat is the cost?carbon dioxideThe CO2 level has soured since when? the industrial revolutionWhat are the effects in the UK?
- 19 of 20 years have been the warmest
- heatwaves
- animals could disappear
How many climate refugees will there be in Britain by 2050? 200 million
When will Fairborn be flooded? 26 years
What are some of the other things that will be 'swallowed by the waves'?
- homes
- building sliding into the sea
- toxic sites at risk
How can we stop climate change?
- replacing gas cylinders
- plant trees
- have electric cars
What ideas are school children having about climate change?
- having a protest
- not having kids
- walking and biking
What is the atmosphere called?
a waste Dump.
What is the last statement the reporter made?
We know what we need to do, we have got the technology. What we lack is the
political will.
What places will be affected? everything
What else do we need to think about? sea levels rising
What other places around NZ will be affected? the islands
What does this do to our drinking water? gets it all salty
What are the main concerns? coastal flooding and coastal erosion
What can we do?
- using electric cars
- walking
- not using air travel as much
What is the one, silver bullet solution? there is none
What is the mix of things we need to start doing?
- use renewables more
- get away from fossil fuels
- use more electric stuff more
What are 3 others you can think of?
- walking to close places
- recycling
- don't litter