AIM: TO LOOK AT THE WATER CYCLE AND HOW CLIMATE CHANGE IS AFFECTING IT.
Definition:
e
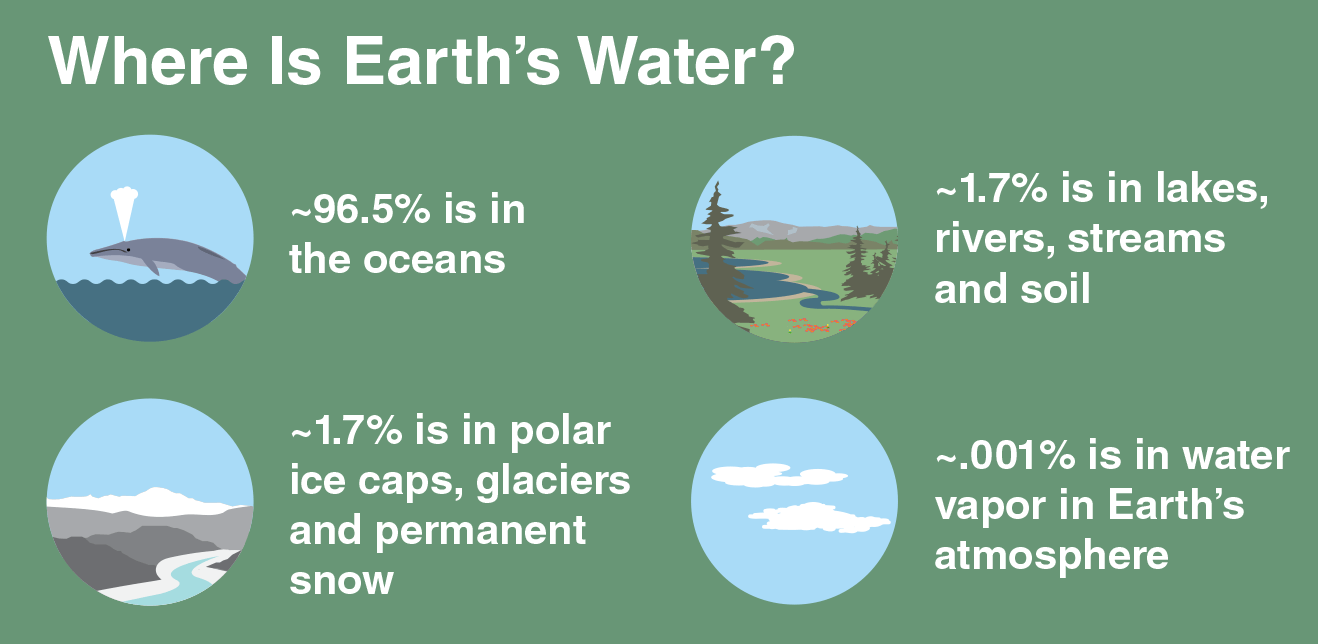
Scientific words:
- Evaporation. When water is heated by radiant energy it turns into water vapor.
- Transpiration. Evaporation from plants.
- Condensation. When water vapor cools, molecules join together and form clouds.
- Precipitation. When clouds get heavy the waters falls as rain, sleet, hail, or snow.
- Acidification: the action or process of making or becoming acidic.
THE WATER CYCLE EXPERIMENT
Bag 1: Normal Water cycle
Bag 2: Water cycle with CO2 added: like Oceans in climate change
Bag 3: Water cycle with ice added: like Antarctica in climate change
Material:
Steps:
Two Images:
Findings:
The Water Cycle: Bag 1
|
CO2 Water Cycle: Bag 2
Acid
|
Desert Water Cycle
Bag 3
| |
Does it cycle?
| |||
Amount of Water
| |||
Acidity
|
Key: Water and acidity amount: 1 = none
2 = small
3 = large
Other comments:
Conclusion:
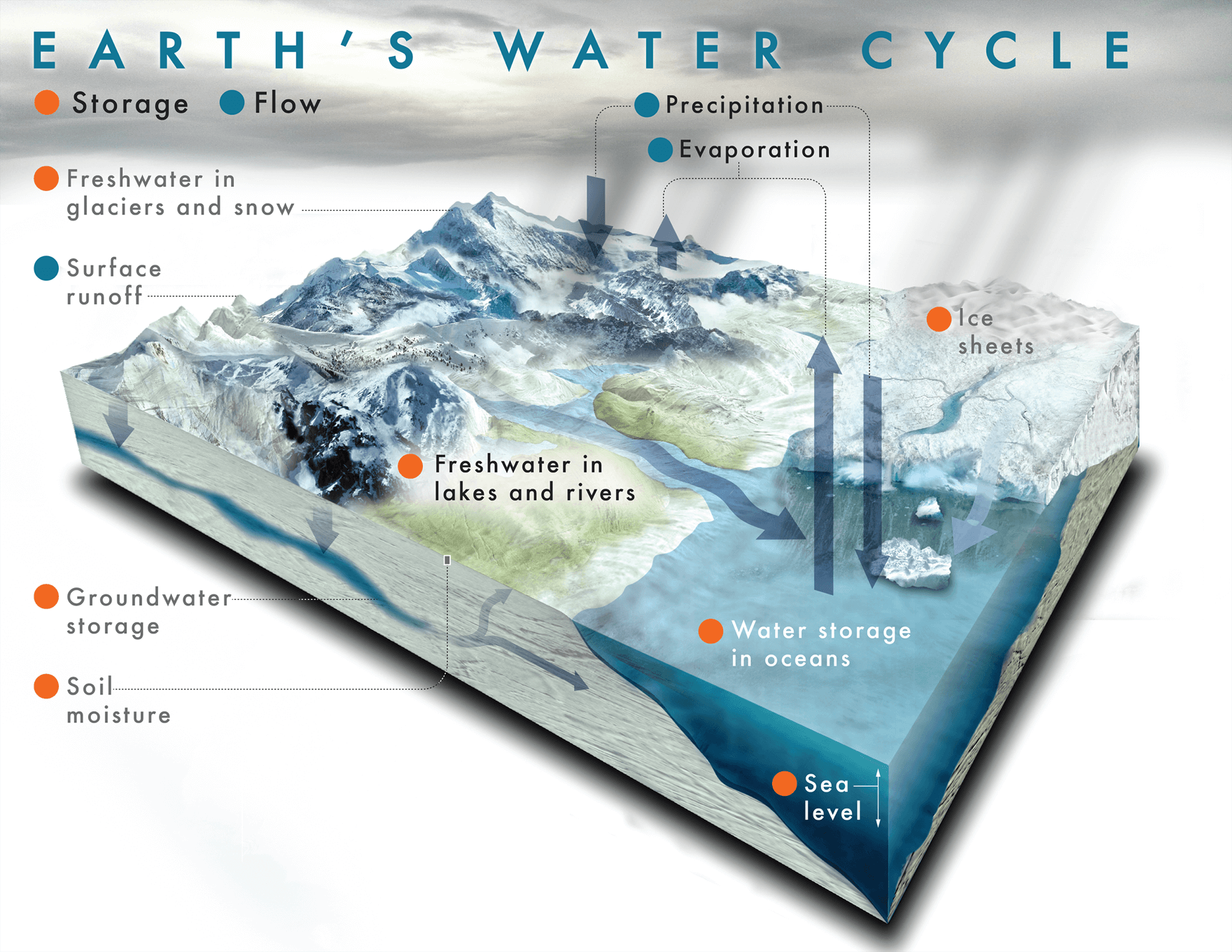
Draw a labelled diagram of the Water Cycle
Water cycle words:
- Precipitation
- Hurricanes
- Acid rain
- Evaporation
- Carbon Dioxide
- Water
- Deforestation
- Water vapour
- Transpiration
- Flooding

No comments:
Post a Comment
To support my learning I ask you to comment as follows:
1. Something positive - something you like about what I have shared.
2. Thoughtful - A sentence to let us know you actually read/watched or listened to what I had to say
3. Something thoughtful - how have you connected with my learning? Give me some ideas for next time or ask me a question.